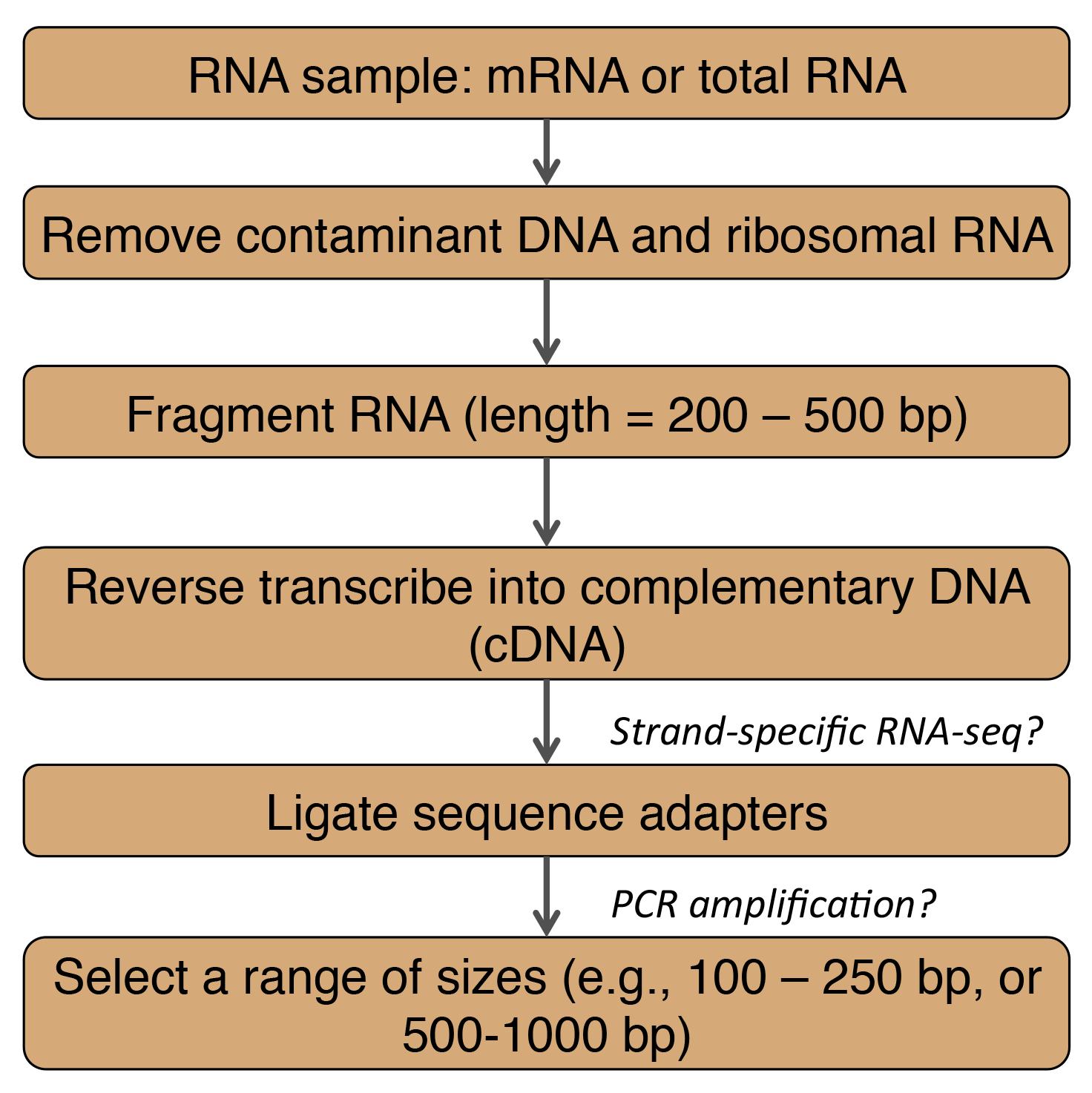
Adapted from Martin and Wang (2011). bp = base pairs
Quality Control: Sample preparation methods
In general, RNA-Seq data are highly accurate and reproducible for both technical and biological replicates (Wang et al., 2009). Thus given a well-documented protocol, RNA-Seq results should be of high quality. However, choices in some of the sample preparation steps may introduce biases for certain transcripts or transcript regions as summarized below.
- mRNA enrichment by polyA selection will miss non-coding RNAs and mRNAs that lack a polyA tail. Quantification of highly abundant transcripts will be biased (Martin and Wang, 2011).
- Fragmentation methods (Wang et al., 2009)
- RNA fragmentation depletes transcripts ends compared to other methods.
- cDNA fragmentation causes a biased identification of sequences from the 3' ends of transcripts.
- PCR amplification results in low sequencing coverage for transcript regions that have a high GC content, which can cause gaps in the assembled transcript (Martin and Wang, 2011).